 I've got a question for you. What the heck is gluten?
I've got a question for you. What the heck is gluten?
We've all heard about gluten, or perhaps more accurately, we've heard the phrase gluten-free. We've heard people talk about how they can't (or won't) eat it. We've seen cookies and crackers and bread marketed as being devoid of gluten.
But what is gluten, exactly, and why do people avoid it?
Here's what I know about gluten. It is largely based on my occasional reading of In Touch Weekly:
- it has something to do with white flour (which is apparently evil, although I'm not sure if this is purely because of gluten)
- if foods do not have gluten, it is ok for them to cost several dollars more
- avoiding gluten is very trendy right now. People who avoid gluten can basically be divided into three camps: people who have a severe reaction to it, people who have an intolerance to it, and people who have eating disorders.
Of course, this is not actual knowledge based on fact. I mean, how many times has that periodical lied about Jen's baby bump and Brangelina's breakup?
Nope: In Touch Weekly is not the source for gluten information. Let's get down some facts not supplied by pop culture periodicals...
Gluten
Dictionary definition: gluten is a general name for the proteins found in wheat (varieties of which include durum, emmer, spelt, farina, farro, kamut, etc) , rye, barley and triticale.
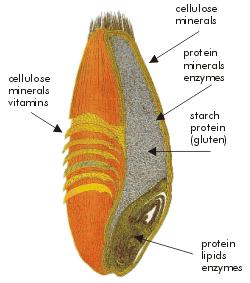 Photo via Professional Pasta Magazine (really)
Photo via Professional Pasta Magazine (really)
Where does the funny name come from? According to Dictionary.com, the origin is such:
1630s, "any sticky substance," from Middle French gluten (16c.) or directly from Latin gluten "glue" (see glue (n.)). Used 16c.-19c. for the part of animal tissue now called fibrin; used since 1803 of the nitrogenous part of the flour of wheat or other grain; hence glutamic acid (1871), a common amino acid, and its salt, glutamate.
What it does in food: Gluten does what its name sounds like: acts as "glue" that holds food together. It helps doughs maintain elasticity and a good "chew". While most people instantly think "flour" when they think of gluten, this is not quite accurate. It's not just baked goods or bread that contain gluten--it can be used in a number of different products to add thickness, texture, or bulk.
This is what makes baking particularly maddening when gluten is taken out of the equation. To get the same texture, taste, and bulk which wheat based flour lends to baked goods, you can't just rely on one type of gluten-free flour. Different mixes are required to meet each of the criteria. If you want more guidance on that, check out this post on Craftsy. You'll also probably enjoy checking out the blogs of my buddies both online and in real life, Gluten-Free Girl and The Art of Gluten-Free Baking to learn more about gluten-free baking.

Primary sources of gluten in your everyday diet:
Wheat, barley, and rye. This triple threat of gluten-containing goodness constitutes a major part of many foods, including but not limited to: bread, cereals, baked goods, pasta, soup, sauces, food coloring, and beer. Gluten can be found in unexpected sources, too, such as soups or sauces that you wouldn't even think of containing flour. However, many of them do contain traces of gluten-containing matter, which gives them structure and thickness. This is why people who need to adhere to a gluten-free diet are forever scanning food labels.
Why would people avoid gluten?
If you have celiac disease, you kind of need to. According to WebMD,
Experts estimate that about 1% of Americans have celiac disease. The condition, caused by an abnormal immune response to gluten, can damage the lining of the small intestine. That, in turn, can prevent important nutrients from being absorbed. Symptoms of celiac disease include diarrhea, anemia, bone pain, and a severe skin rash called dermatitis herpetiformis.
Aside from that, though, some people simply feel better when they avoid gluten. It doesn't cause a death threat, but it can cause discomfort. Others perceive it to be a healthier way to be, or a way to lose weight.
As WebMD further says,
Gluten itself doesn’t offer special nutritional benefits. But the many whole grains that contain gluten do. They’re rich in an array of vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins and iron, as well as fiber. Studies show that whole grain foods, as part of a healthy diet, may help lower risk of heart disease, type-2 diabetes, and some forms of cancer. The 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that half of all carbohydrates in the diet come from whole grain products.
Whew! If you feel like you'd like more GF info, check out these posts I did for Craftsy:
